A scientific study led by Mahyar Etminan, titled “Association Between Sublingual Buprenorphine-Naloxone Exposure and Dental Disease,” investigates the risk of long-term usage of sublingual buprenorphine-naloxone.

The findings published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) suggest a notable correlation between the use of sublingual buprenorphine-naloxone (Suboxone) and an increased frequency of dental issues compared to other opioid addiction treatment methods.
The actions taken by Indivior to launch a generic version of its Suboxone sublingual film “at-risk” in collaboration with a subsidiary of Novartis displays a strategic approach to preserve a multi-billion dollar annual market share.
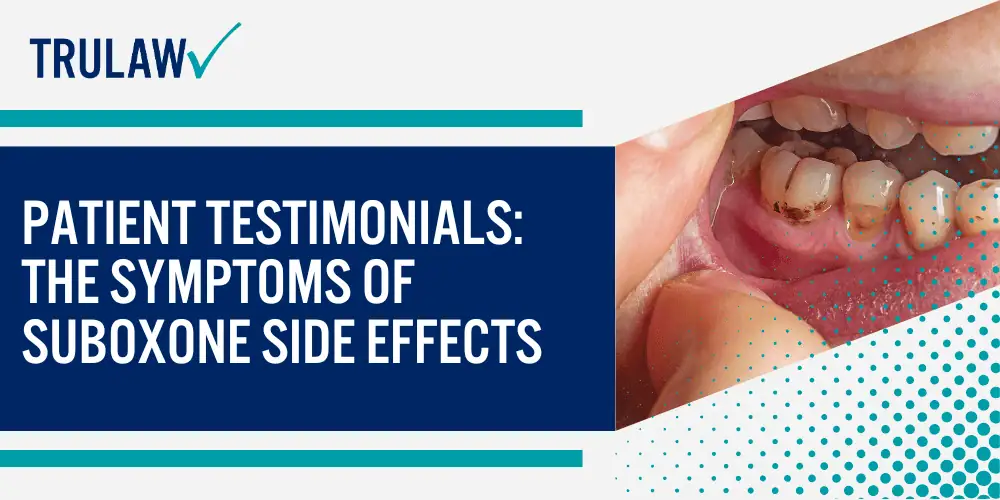
Negative Dental Health Effects: Suboxone Sublingual Strips
The analysis utilized data from the PharMetrics database, encompassing patient records from 2006 to 2020, to create a cohort of new users to treat opioid addiction.
Key findings from the research led by Mahyar Etminan include:
- Increased Dental Adverse Events: Sublingual buprenorphine-naloxone users saw a higher rate of dental adverse events, 21.6 per 1000 person-years, versus 12.2 for transdermal buprenorphine medications and 10.9 for oral naltrexone users per 1000 person-years.
- Higher Incidence of Caries or Tooth Loss: Specifically, the rate for dental caries or tooth loss was 8.2 per 1000 person-years among sublingual buprenorphine-naloxone users, compared to 3.5 and 3.8 per 1000 person-years for transdermal buprenorphine and oral naltrexone users, respectively.
- Significantly Elevated Risk: Adjusted analyses showed a statistically significant higher risk of severe dental injuries for patients using Suboxone compared to alternatives.
The study uncovers a notable concern that the acidic properties of sublingual buprenorphine-naloxone, combined with its application under the tongue, could potentially lead to dental damage.
This research highlights the importance of including dental health within the comprehensive care plan for patients undergoing treatment with sublingual buprenorphine-naloxone (Suboxone) for opioid addiction.